
A language modeling approach to information retrieval. International World Wide Web Conferences Steering Committee, 2016. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference Companion on World Wide Web, pages 83-84. Improving document ranking with dual word embeddings. In Advances in neural information processing systems, pages 3111-3119, 2013. Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space. In Proceedings of the 27th annual international ACM SIGIR conference on Research and development in information retrieval, pages 186-193. Cluster-based retrieval using language models. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pages 2177-2185, 2014. Neural word embedding as implicit matrix factorization. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-14), pages 1188-1196, 2014. Distributed representations of sentences and documents. In Proceedings of the 16th annual international ACM SIGIR conference on Research and development in information retrieval, pages 191-202. Viewing morphology as an inference process. In Proceedings of the 23rd ACM International Conference on Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, pages 111-120. A comparison of retrieval models using term dependencies. In Proceedings of the 22nd annual international ACM SIGIR conference on Research and development in information retrieval, pages 50-57.

Twenty-one at trec-7: Ad-hoc and cross-language track. In Proceedings of the 38th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pages 795-798. Word embedding based generalized language model for information retrieval. Document embedding with paragraph vectors. Latent semantic indexing (lsi) fails for trec collections. In Proceedings of the 39th annual international ACM SIGIR conference on Research and development in information retrieval. Improving language estimation with the paragraph vector model for ad-hoc retrieval. The three issues we address are (1) the unregulated training process of PV is vulnerable to short document over-fitting that produces length bias in the final retrieval model (2) the corpus-based negative sampling of PV leads to a weighting scheme for words that overly suppresses the importance of frequent words and (3) the lack of word-context information makes PV unable to capture word substitution relationships. We also describe modifications to the model that make it more suitable for the IR task, and show their impact through experiments and case studies.
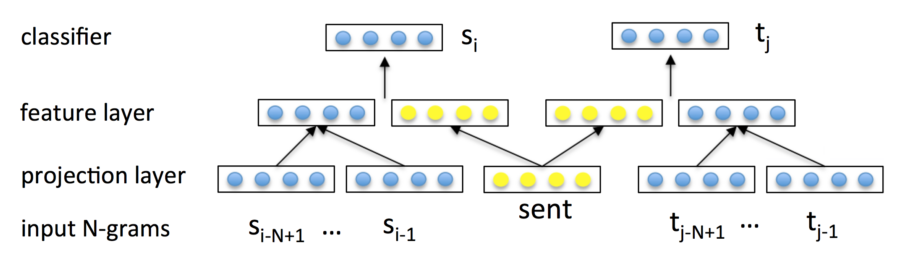
In this paper, we formally discuss three intrinsic problems of the original PV model that restrict its performance in retrieval tasks. Integrating the PV models with traditional language model approaches to retrieval, however, produces unstable performance and limited improvements. In particular, paragraph vector (PV) models have shown impressive performance in some natural language processing tasks by estimating a document (topic) level language model. Previous studies have shown that semantically meaningful representations of words and text can be acquired through neural embedding models.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
